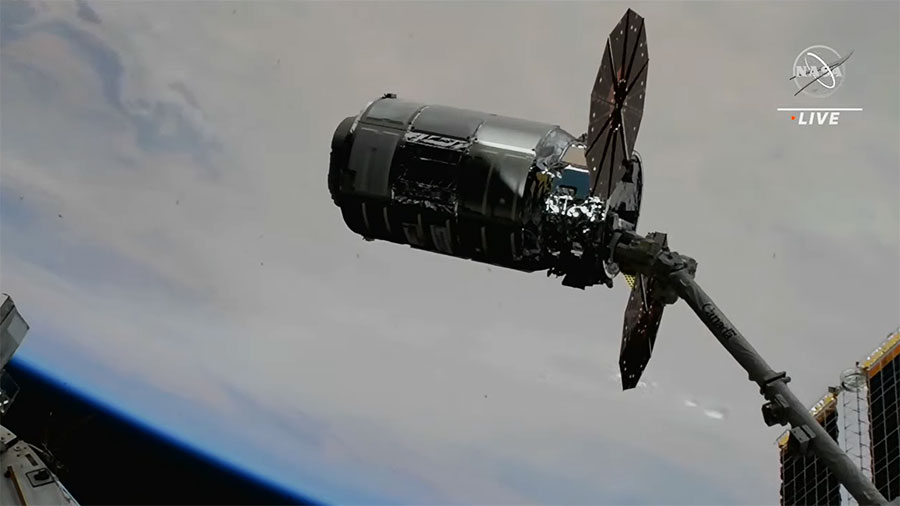
At 7:07 a.m. EDT, flight controllers on the ground sent commands to release the Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft from the Canadarm2 robotic arm after earlier detaching Cygnus from the nadir port of the International Space Station’s Unity module. At the time of release, the station was flying about 260 miles over the Pacific Ocean.
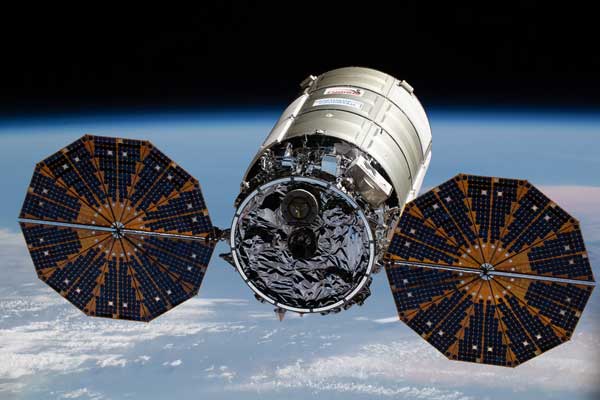
The Cygnus spacecraft successfully departed the space station more than three months after arriving at the microgravity laboratory to deliver about 8,300 pounds of supplies, scientific investigations, commercial products, hardware, and other cargo for NASA.
Following a deorbit engine firing on Wednesday, June 29, Cygnus will begin a planned destructive re-entry, in which the spacecraft – filled with trash packed by the station crew – will safely burn up in Earth’s atmosphere.
Cygnus arrived at the space station Feb. 21, following a launch on Northrop Grumman’s Antares rocket from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on Wallops Island, Virginia. It was the company’s 17th commercial resupply services mission to the space station for NASA. Northrop Grumman named the spacecraft after the late NASA astronaut and climate scientist Piers Sellers.
On Saturday, June 25, Cygnus completed its first limited reboost of the International Space Station. Cygnus’ gimbaled delta velocity engine was used to adjust the space station’s orbit through a reboost of the altitude of the space station. This Cygnus mission is the first to feature this enhanced capability as a standard service for NASA, following a test of the maneuver which was performed in 2018 during Cygnus’s ninth resupply mission.
Learn more about station activities by following the space station blog, @space_station and @ISS_Research on Twitter, as well as the ISS Facebook and ISS Instagram accounts.
Get weekly video highlights at: http://jscfeatures.jsc.nasa.gov/videoupdate/
Get the latest from NASA delivered every week. Subscribe here: www.nasa.gov/subscribe




